
Circular Economy
Adopting practices dealing with reverse logistics and waste reduction, recycling and resource recovery in logistics.
Theme: Sustainability
Industry Adoption: ⚫ ⚪ ⚪ ⚪ Early stage
Impact: ⚫ ⚪ ⚪ Moderate
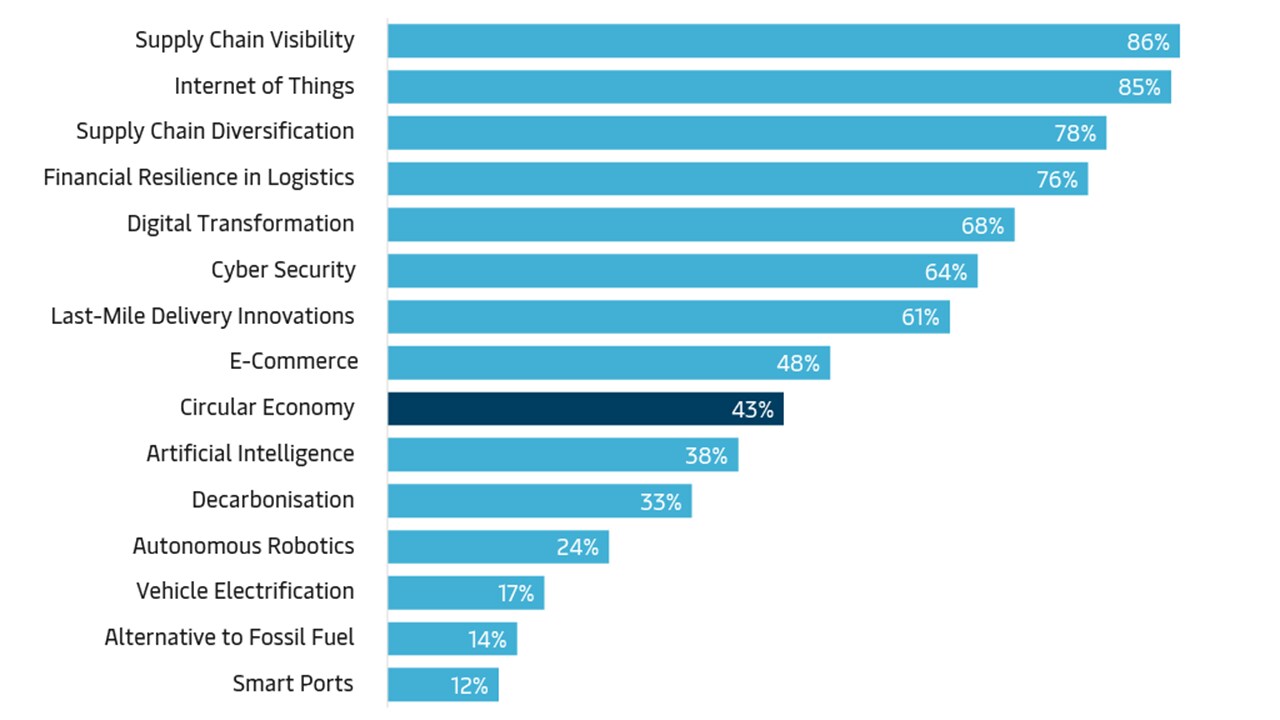
A 2024 Maersk survey shows that decision makers rank Circular Economy 9th out of the top 15 trends.
Circular economy focuses on adopting new practices to embed circularity throughout logistics operations. Key actions include reverse logistics, which coordinates the transport of returned products to distribution centres for reuse or recycling, as well as waste reduction and transformation to minimise environmental impact during storage and transit. Extracting value from end-of-life products, such as recovering rare metals from used batteries transported to specialised facilities, further enhances the role of logistics in supporting circularity. Waste production is expected to reach 2.59 billion tonnes by 2030, increasing to 30% by 2050. Circular economy addresses the environmental challenges of linear models, including rising waste and low recycling rates.
~20
thereof groundbreaking: 100+
2024: 120+

Explore the Global Logistics Trends of 2025
Dive deep into the Top 10 trends shaping the industry today as well as valuable insights to help you build a more resilient supply chain.
This trend aligns with sustainability and climate change megatrends, drawing media attention, yet industry adoption lags as companies remain cautious. Since 2015, around 20 startups have emerged, signaling moderate activity. From 2019 to 2023, 1,500 patents, including over 100 groundbreaking innovations were filed, showcasing opportunities for advancement. C-Suite mentions declined from 180 in 2022 to 120 in 2024, which in this case reflects restrained executive focus. Academic interest is strong, with about 7,000 publications.
Top 15 Trends
Share of Key Decision Makers, who consider the trend to be relevant for their company’s logistics
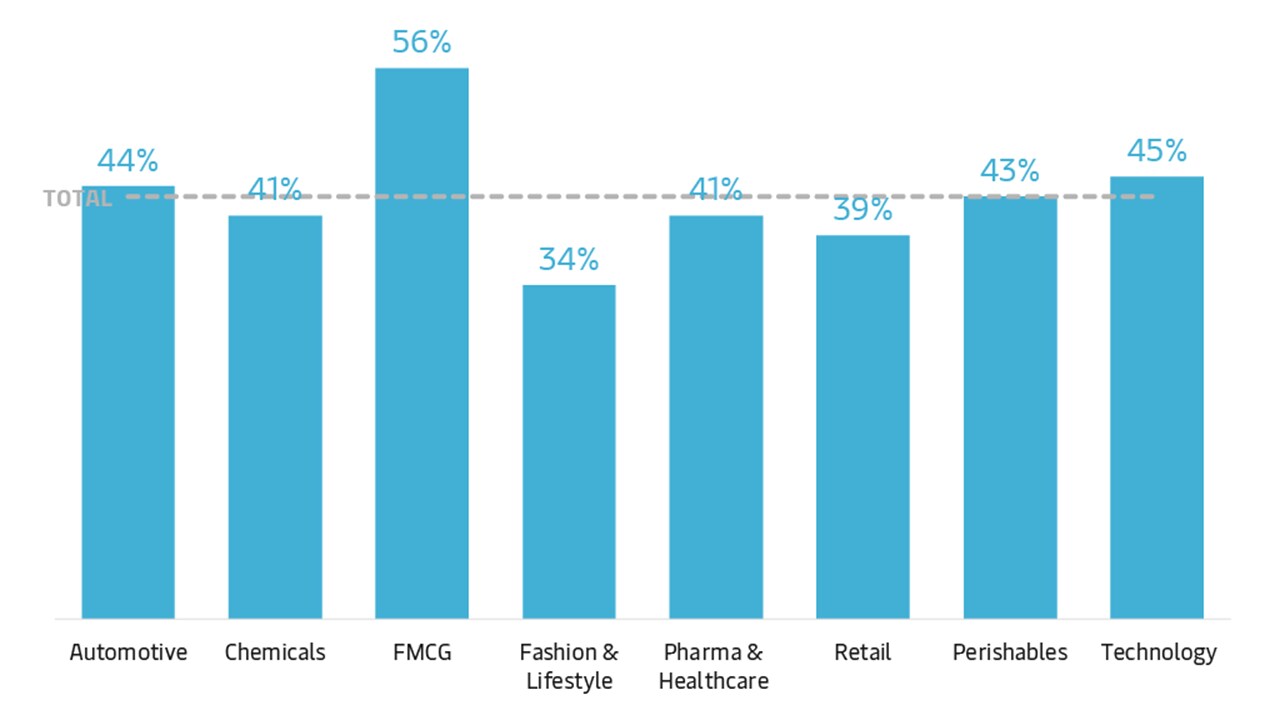
Circular Economy – Relevance by Industry
What are the opportunities?
Integrating circular economy processes into corporate logistics reduces GHG emissions, strengthens customer trust, and unlocks new revenue streams. This includes reselling returned goods as second-hand products, extending product lifecycles, and improving packaging to minimise returns and lower costs.
What are the challenges?
Implementing circularity in logistics comes with challenges such as high investment costs for establishing reverse logistics, balancing customer expectations for free returns, navigating complex regulations and ensuring seamless integration of circular processes through advanced planning and analytics.
Sources:
- Statista (2018).
- Survey among 500+ global logistics decision makers across various industries, conducted by Statista for Maersk (Q4 2024).
- In-depth interviews with global industry experts, academia, and futurists.
- Unstructured web sources with more than 10,000 search term permutations using AI.
- Curated data from startup databases, patent databases, and analysis tools, as well as Semantic Scholar.


